The emergence of cash requirement without any hustle and increased adaptation to digital complemented with push to promote paperless, cashless and delivery without being present paves the way for the emergence on the concept Open Credit Enablement Networks (OCEN).
It also allows new MSME entrepreneurs to play an emerging role in the lending value chain which in short, is a completely new credit ecosphere of India.
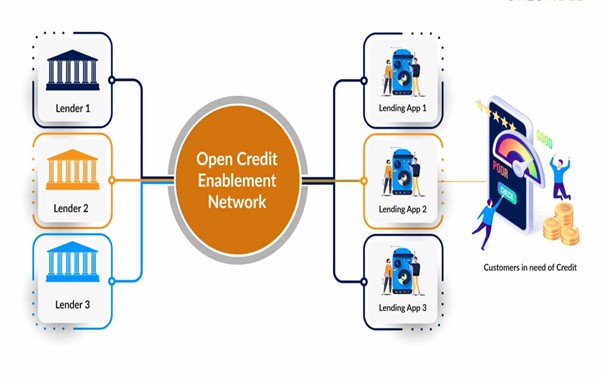
Open Credit Enablement Networks (OCEN) function by merging and automating the different manual processes involved in a lending value chain, such as the screening of loan-worthy customers, and the onboarding of new borrowers, thus decreasing the total operating costs of them and increasing their effectiveness. OCEN is a protocol that allows platforms and markets called LSPs (Loan Service Providers) to link to banks and non-bank lenders to digitize the origination, underwriting, and servicing process of loans. In this context, Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN) has appeared as a novel lending paradigm and a protocol infrastructure that would help in the facilitation of interoperability between Loan Service Providers (LSPs), like FinTech and E-commerce players, and traditional lenders, like banks and Non-Bank Financial Companies (NBFCs). The next big opportunity for fintech through this open credit network is for lenders to get willing to interact with LSPs based on a new lending protocol infrastructure.
Once OCEN is launched at total ability, experts say that not only will it digitize the entire loaning process, but it will also make it easier to access credit to all, particularly individuals and MSMEs. The OCEN Framework will take advantage of digital initiatives such as the Aadhaar-based eKYC and Account Aggregators, enabling robust infrastructure for financial institutions to efficiently and profitably service end-borrowers. By democratizing access to credit, a new credit protocol infrastructure addresses multiple pain points in India’s lending industry, such as reducing costs for acquiring new customers, shortening turnaround time for loan deposits, lowering interest rates, and streamlining the requirements for loans, etc. As the Indian credit ecosystem continues to grow through fast digitalization, it is expected that this protocol will play a pivotal role in the decentralization of credit to low-resource Indian borrowers.
The OCEN protocol provides a standardized set of APIs, so apps already working with individuals and MSMEs can efficiently integrate credit capabilities into their existing products and services offerings. By activating these OCEN-enabled markets as sources for finding customers and supplying loans, OCEN will allow several new types of lending offerings. By adding the layer of OCEN and current digital ecosystems to the top, the marketplaces and e-commerce platforms are ideal to deliver credit to underserved populations via innovative embedded financial solutions.
In simpler terms, OCEN can be understood as a software architecture that brings the different stakeholders in the credit ecosystem together under a single roof, through APIs and intelligent integrations, thus enabling lenders to build tailored lending instruments, and businesses to simplify their access to the market that hosts a broad array of credit products. The ultimate objective OCEN looks to carry out with its painstakingly crafted, but the optimized approach is the democratization of lending, ensuring credit is accessible to anyone and everyone who needs credit. With OCEN, lenders will be positioned to use fast, standardized loan data to take a more proactive, efficient approach to compliance, lending decisions, disbursements, assessing creditworthiness, and risk management functions. Finally, OCEN gives lenders the opportunity to expand their markets and offer innovative lending products, reducing their acquisition costs.
Concisely, OCEN has the potential to revolutionize MSME financing in India if it is executed well. The digital network that will be created using the blueprint may encourage improved service for the MSME borrower by harnessing the technological acumen of multiple players, including LSPs, TSPs and lenders.
By 2030, India’s financial sector will generate $200 billion in revenue and generate $1 trillion worth of financial products. The well-regulated and well-funded sector is teaming up with growing smartphone penetration and a younger generation in a country recognized as a hub for entrepreneurs.
In fact, the fintech industry would be home to 17 of India’s 100 unicorn firms, and between 2022 and 2028, the fintech ecosystem is expected to snowball, with a CAGR of 6.3%.
Two other prominent DPGs in India that has gained much traction and reach are Aadhaar and UPI (United Payments Interface). There seems to be every reason to believe that OCEN would be the next UPI moment for MSME lending in India!
MSMEs will have more flexibility of choice and a secure, pragmatic option for obtaining government finance. The loan application process will be streamlined, and credit underwriting will place less emphasis on outmoded methods like credit history research and more emphasis on factors like a company’s steady cash flow.
The implementation of OCEN will eventually have a substantial beneficial effect on MSME and the country’s GDP.

(This article is written by Vinishadevi, Audit Executive at R V K S And Associates)